45 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
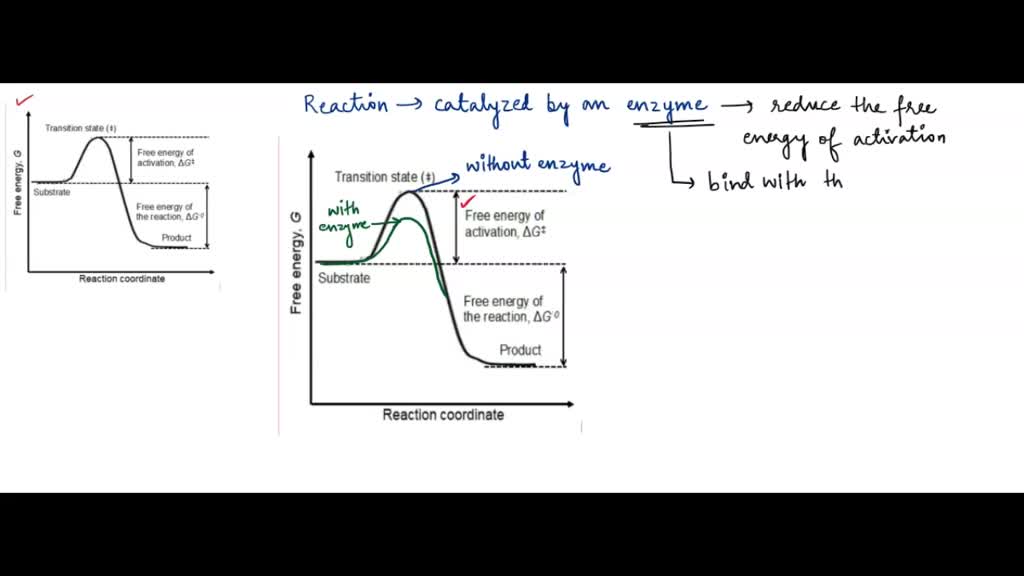
Answered: Sketch a qualitative reaction energy… | bartleby Sketch a qualitative reaction energy diagram for a chemical reaction with and without a catalyst. Assume the uncatalyzed reaction is endothermic. Note: Because the sketches are only qualitative, the energies in them don't have to be exact. They only have to have the right relationship to each other. IOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR B EDUCATION Printed in U.S.A. Articles Energy ... Energy Diagrams for Enzyme-catalyzed Reactions CONCEPTS AND MISCONCEPTS Received for publication, March 20, 2003, and in revised form, April 21, 2003 ... a negative value for the free energy change of the global process is a necessary requisite, but it is not sufficient. ... depicted in blue and red for the uncatalyzed and catalyzed reac-tion ...
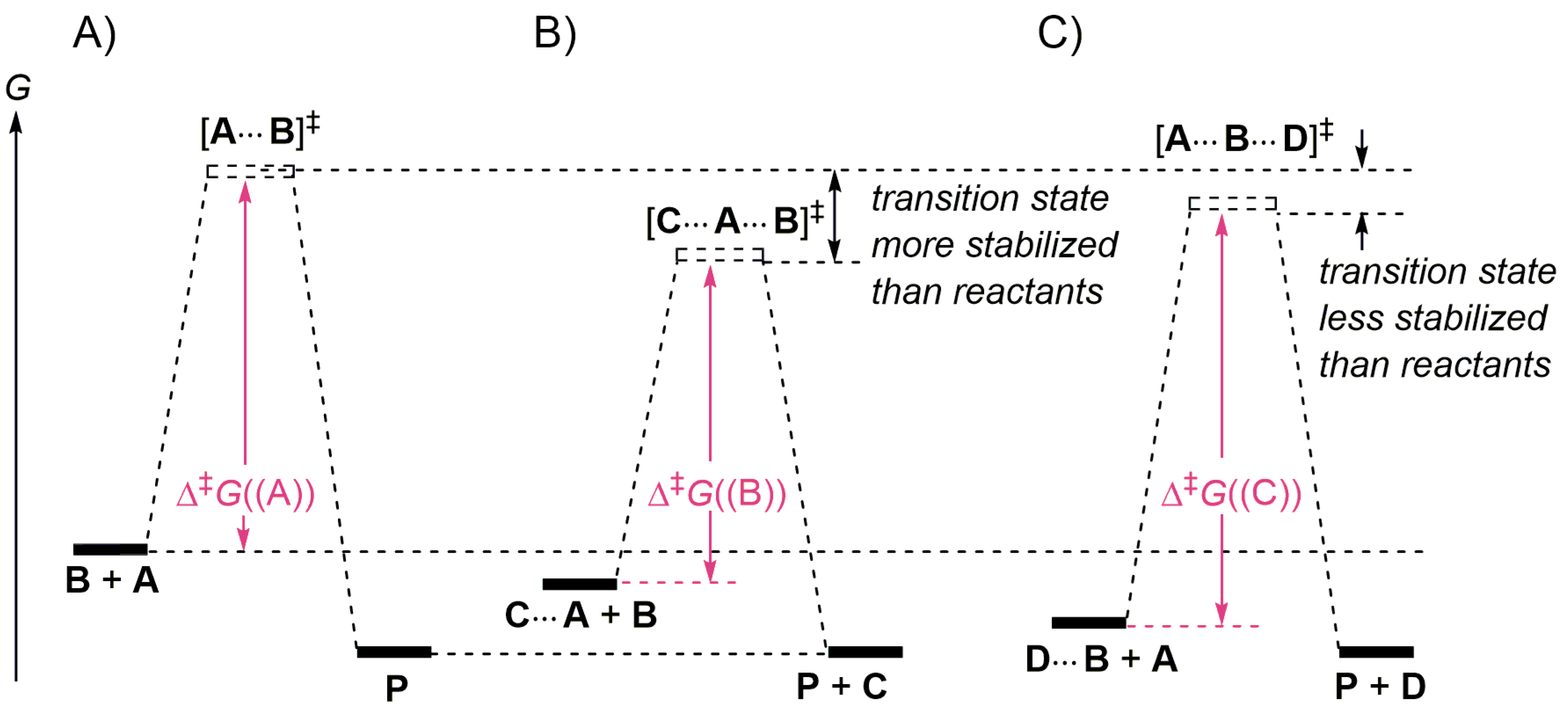
PDF Energy/Reaction Coordinate Diagrams - chemconnections A Reaction Coordinate (Energy) Diagram Thermodynamic Quantities Gibbs standard free energy change (ΔGo) Enthalphy (ΔHo): the heat given off or absorbed ... Bonds are NOT in the process of breaking or forming. ! Energy Diagrams # Intermediates! 6! For each of the diagrams below, will the transition state
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process
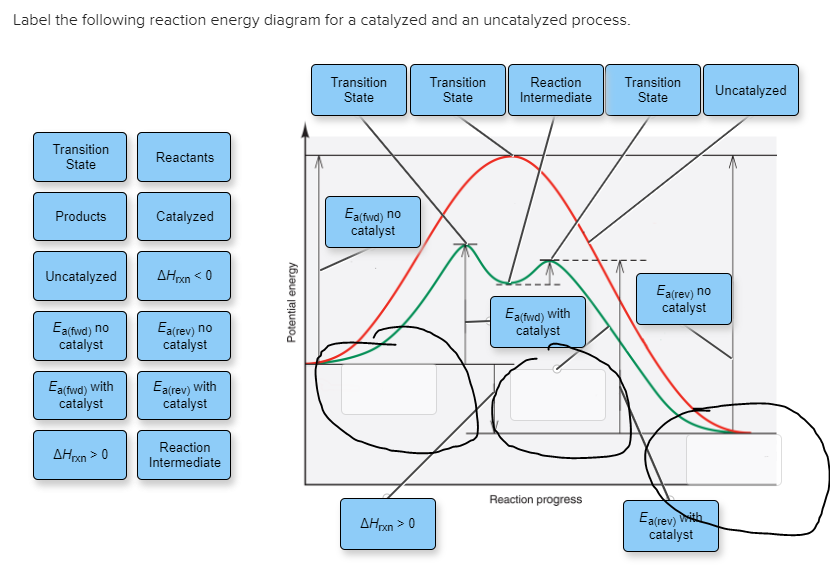
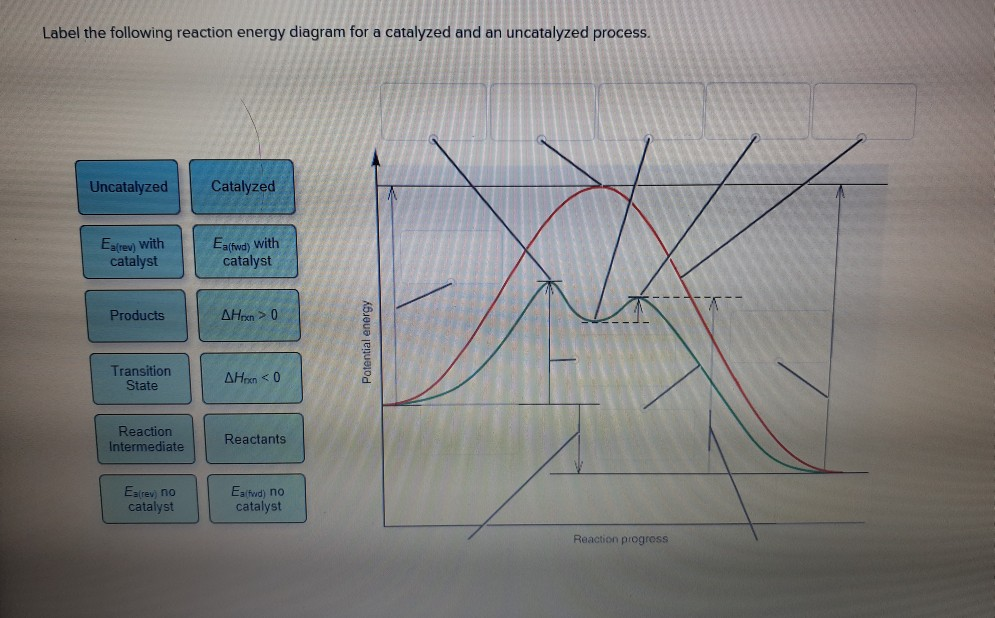
Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Question: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. A > 0 Eatwa) no catalyst Exter, with catalyst Reactants Esinev) no Eastw with catalyst Potential energy Mono Products Uncatalyzed Catalyzed Transition State Reaction Intermediate Reaction progress Reset Zoom This problem has been solved! See the answer tillery 8.25 Use energy diagrams to compare catalyzed and uncatalyzed ... Below is a figure depicting the energy diagram of a reaction. Both uncatalyzed and catalyzed version of the reaction are shown. Use the figure to answer the following questions. 5 1 AAG (the reduction in AG by the catalyst) G 2 3 A+B=P+Q Reaction coordinate a. Number 4 corresponds to which of the following? a. Products (P+) b. 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 112- Chapters 12-17 of OpenStax ... - Unizin A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation.
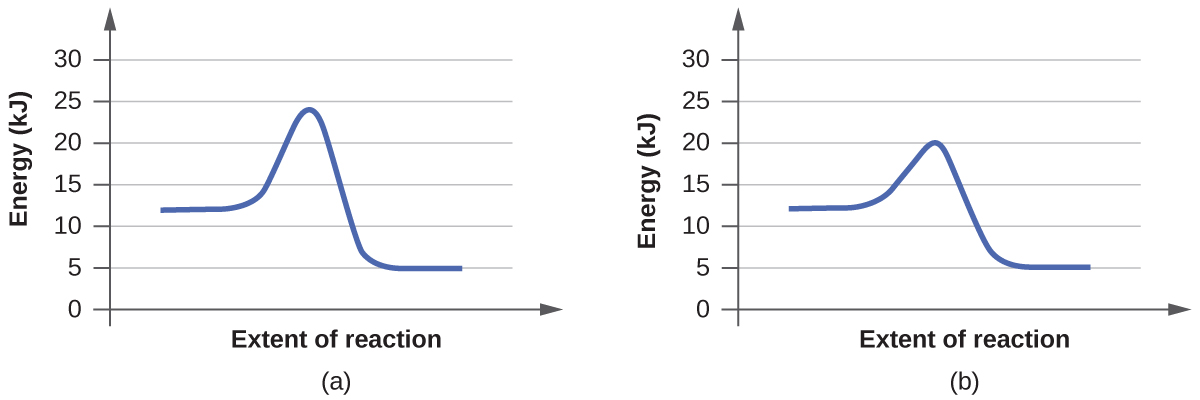
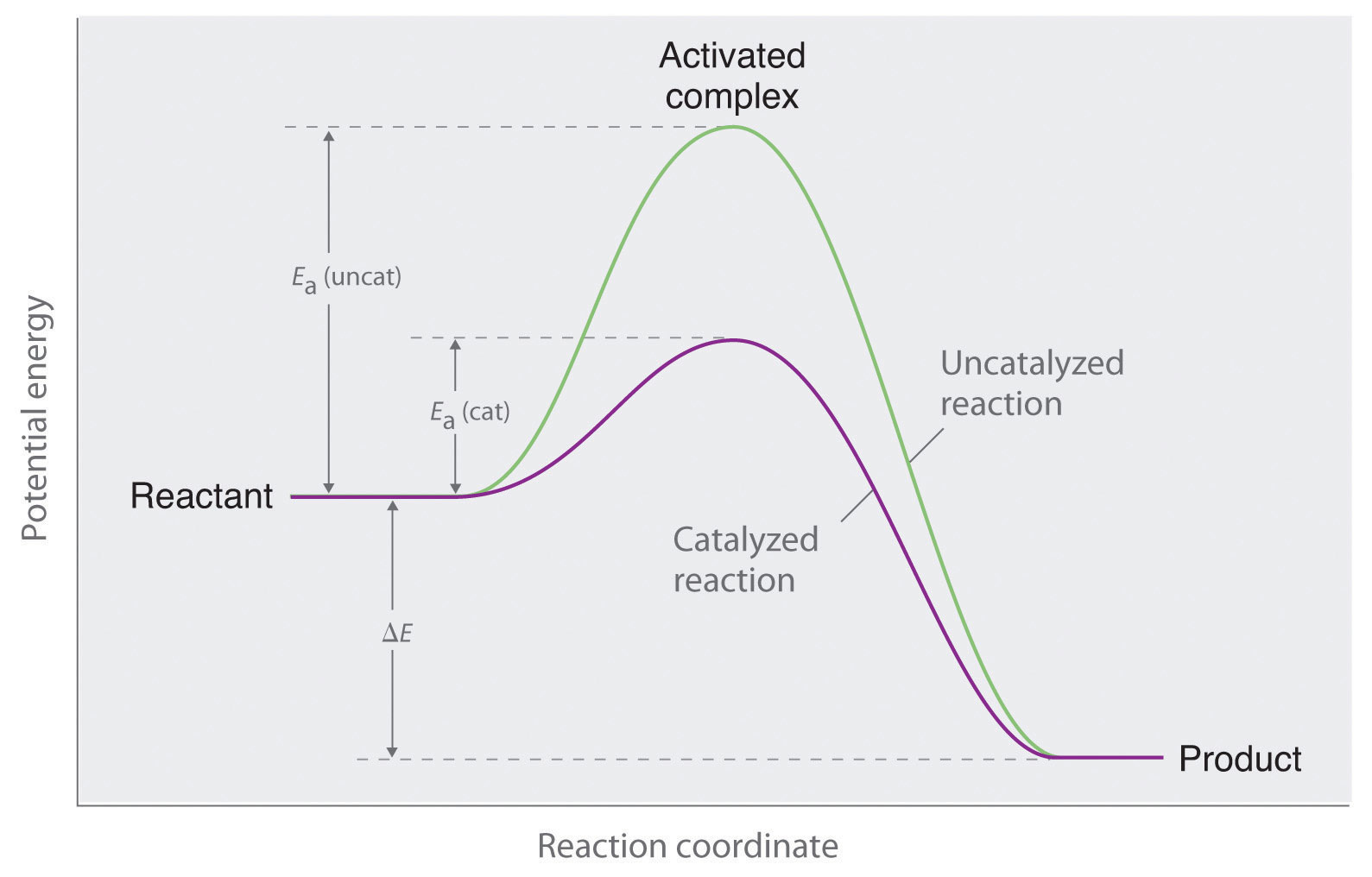
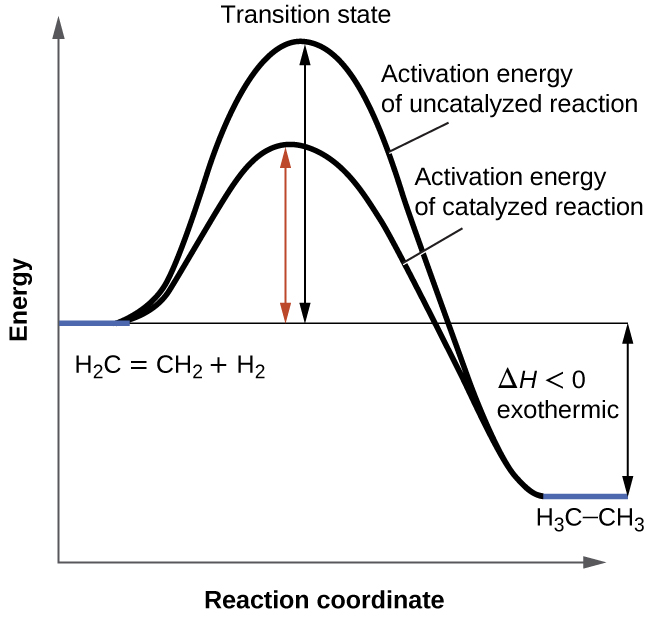
Reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Catalysts Definition and How They Work - ThoughtCo A catalyst is not consumed by the reaction and it may participate in multiple reactions at a time. The only difference between a catalyzed reaction and an uncatalyzed reaction is that the activation energy is different. There is no effect on the energy of the reactants or the products. The ΔH for the reactions is the same. How Catalysts Work Energy Changes in Catalytic Reactions - QS Study A catalyst provides a different route with lower activation energy. Fig: Energy diagram for unanalyzed and catalyzed reactions. In Figure, the unanalyzed reaction is shown as a single step with high energy of activation. The catalyzed reaction is shown as a two-stage process with lower activation energy and is, therefore, faster. Catalysis - Chemistry - University of Hawaiʻi One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in . 12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 2e | OpenStax For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
4.6 Catalysis - Inorganic Chemistry for Chemical Engineers - BCcampus For the first step, Ea = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants. energy diagram catalyzed vs uncatalyzed reaction The energy diagram for a uncatalyzed reaction is an alternative way to describe a reaction. It's just a graph that shows the concentration of the reactant as well as the product. If your reaction isn't catalyzed, then the energy diagram will show this, meaning that the reaction has an exothermic reaction. PDF Reaction Rates and Catalysts in Ethanol Production (One Activity) - Energy • Students will be able to interpret and draw reaction progress diagrams for catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions. Time Allotted . Five 45 minute periods are needed to complete the entire module. Any of the days can be combined to accommodate block scheduling. The break down is: Day 1: Introduction Day 2: Lab, part 1 Day 3: Lab, part 2 Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Transcribed image text: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. Transition State Transition State Transition intermediate Reaction Intermediate Transition State Transition Uncatalyzed Transition State Reactants Products Catalyzed Ea(fwd) no catalyst Uncatalyzed AHxn < 0 Potential energy Ea(rev) no catalyst Ea(fwd) no catalyst Ea(rev) no catalyst ...
Catalysis | Chemistry for Majors - Lumen Learning The uncatalyzed reaction proceeds via a one-step mechanism (one transition state observed), whereas the catalyzed reaction follows a two-step mechanism (two transition states observed) with a notably lesser activation energy. PDF Graph Review - ISD 622 Below is an energy diagram for a particular process. One curve represents the energy profile for the uncatalyzed reaction, and the other curve represents the energy profile for the catalyzed reaction. Course reaction a. N%ich curve has the geater activation energy? Curve 1 or cunre 2? b. SOLVED:Label the following reaction energy diagram for catalyzed and an ... VIDEO ANSWER:let's just ask this question. So here we need to label the following reaction energy diagram for the capitalized and unfertilized process. So let's draw this diagram. You know, we have this and here four C. This will be the levels open up McGee. So here we have an arrow, you will be in the middle, this will be the end over here and curie and So this would be the final 11 that we ... SOLVED: Sketch a reaction energy diagram for an endothermic reaction ... SOLVED: Sketch a reaction energy diagram for an endothermic reaction that has both a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed pathway label the axes, the pathway for the catalyzed and uncatalyzed reaction. and indicate the positions of reactant product and transition state Join for Free MH Melissa H. Chemistry 101 3 months, 2 weeks ago
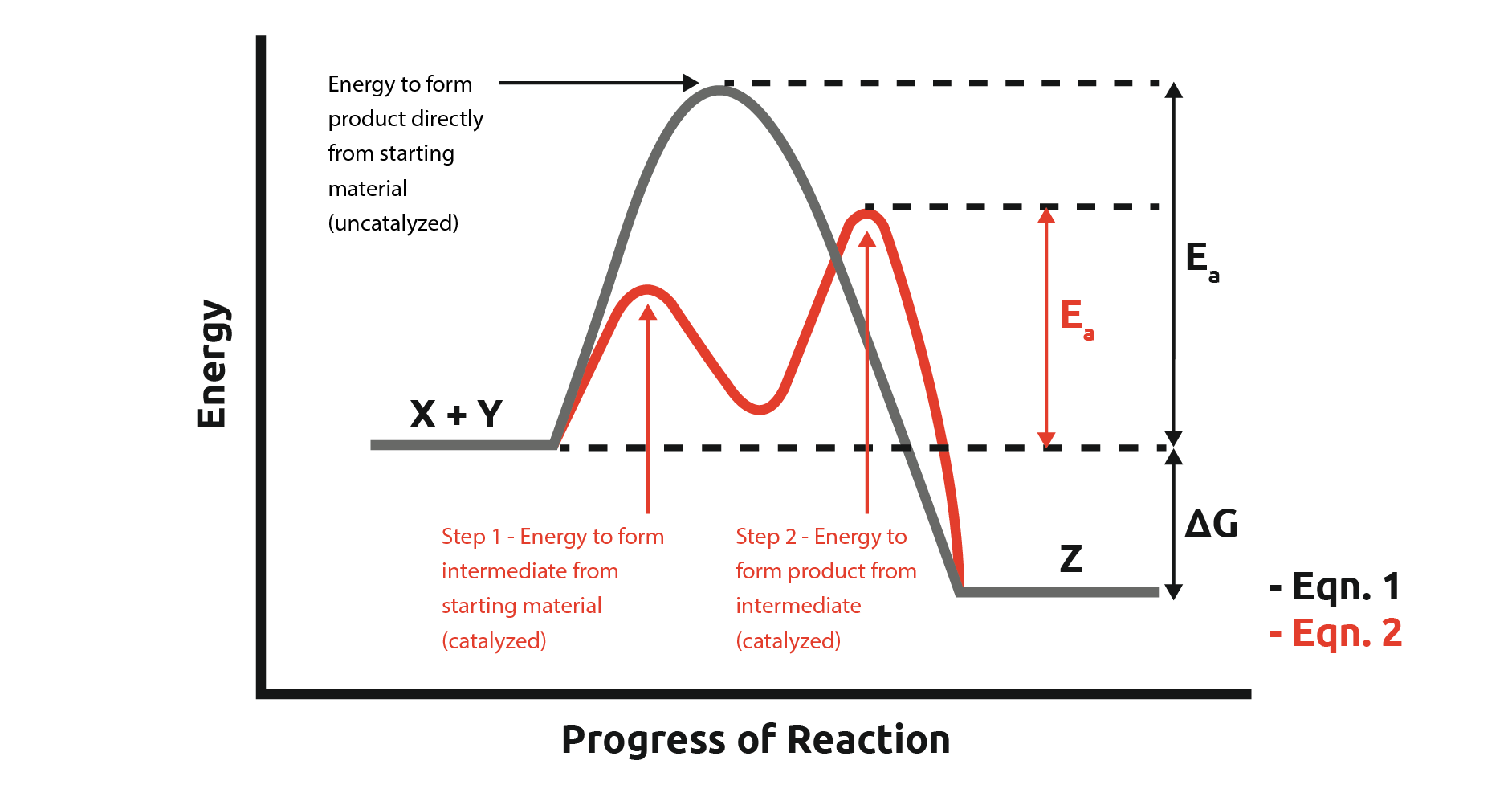
Mechanisms and Potential Energy Diagrams - Course Hero The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the figure is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled E a1 and E a2 .Each elementary step has its own activated complex, labeled AC 1 and AC 2 .Note that the overall enthalpy change of the reaction is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states.
enzyme catalyzed reaction diagram - thesolutionsunit.com Glycolysis is an almost universal central pathway of glucose catabolism. During glycolysis some of the free energy is released and conserved in the form of ATP and NADH. substrate. Example 1: Using Reaction Diagrams to Compare Catalyzed Reactions. It is not permanently used up; thus, it acts as a catalyst.
Energy diagrams for enzyme‐catalyzed reactions: Concepts and ... - IUBMB The energy diagram for a reaction model consisting of one enzyme, one substrate, and one product is depicted in many books where it is compared with that for the uncatalyzed reaction. The survey of several Biochemistry textbooks reveals a high diversity of profiles for the same process. A, C, and D are adapted from Refs. 5, 3, and 2, respectively.
what is the difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions what is the difference between catalyzed and uncatalyzed reactions ...
1 point The plot below shows the energy diagram for a catalyzed (red ... Below is a figure depicting the energy diagram of a reaction. Both uncatalyzed and catalyzed version of the reaction are shown. Use the figure to answer the following questions. 5 1 AAG (the reduction in AG by the catalyst) G 2 3 A+B=P+Q Reaction coordinate a. Number 4 corresponds to which of the following? a. Products (P+) b.
Reaction Kinetics: Reaction Mechanisms - SparkNotes The activation energy of a reaction represents the difference in energy between the reactants and the highest point on a reaction coordinate diagram. We will derive the Arrhenius Equation, which relates the rate constant for a reaction to its activation energy. Local minima on the reaction coordinate diagram are positions occupied by intermediates.
Catalysis (12.7) - Chemistry 110 - Unizin Answer: For the first step, E a = 80 kJ for (a) and 70 kJ for (b), so diagram (b) depicts the catalyzed reaction. Activation energies for the second steps of both mechanisms are the same, 20 kJ. Homogeneous Catalysts A homogeneous catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants.
12.7 Catalysis | Chemistry - Lumen Learning One such reaction is catalytic hydrogenation, the process by which hydrogen is added across an alkene C=C bond to afford the saturated alkane product. A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1.
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry 112- Chapters 12-17 of OpenStax ... - Unizin A comparison of the reaction coordinate diagrams (also known as energy diagrams) for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation is shown in Figure 1. Figure 1. This graph compares the reaction coordinates for catalyzed and uncatalyzed alkene hydrogenation.
tillery 8.25 Use energy diagrams to compare catalyzed and uncatalyzed ... Below is a figure depicting the energy diagram of a reaction. Both uncatalyzed and catalyzed version of the reaction are shown. Use the figure to answer the following questions. 5 1 AAG (the reduction in AG by the catalyst) G 2 3 A+B=P+Q Reaction coordinate a. Number 4 corresponds to which of the following? a. Products (P+) b.
Solved Label the following reaction energy diagram for a - Chegg Question: Label the following reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process. A > 0 Eatwa) no catalyst Exter, with catalyst Reactants Esinev) no Eastw with catalyst Potential energy Mono Products Uncatalyzed Catalyzed Transition State Reaction Intermediate Reaction progress Reset Zoom This problem has been solved! See the answer














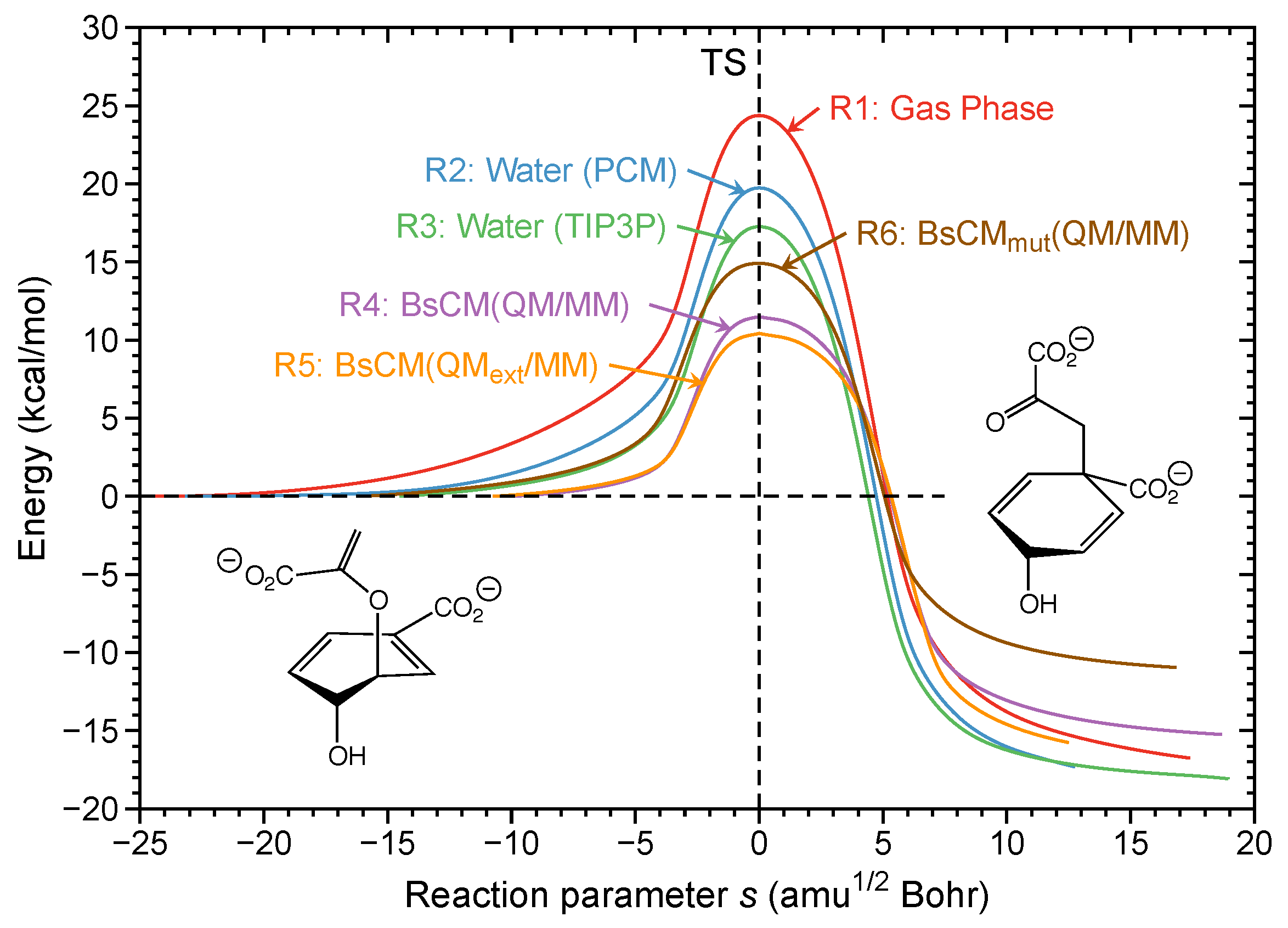
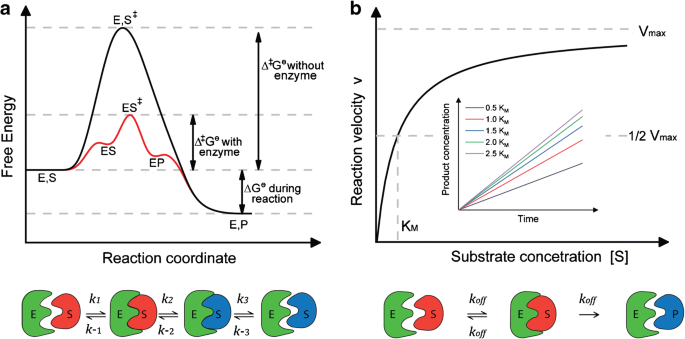



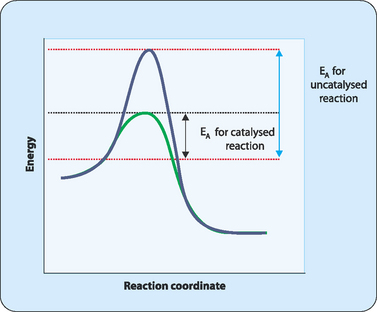


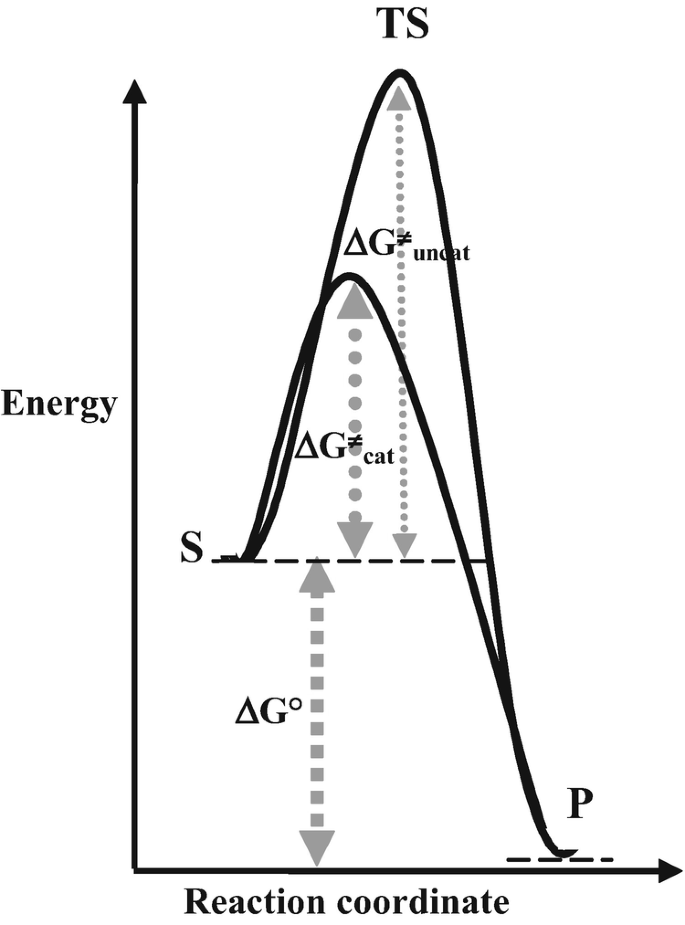








Post a Comment for "45 reaction energy diagram for a catalyzed and an uncatalyzed process"