39 vector biology definition
› genetics-glossary › VectorVector - Genome.gov Apr 26, 2023 · A vector, as related to molecular biology, is a DNA molecule (often plasmid or virus) that is used as a vehicle to carry a particular DNA segment into a host cell as part of a cloning or recombinant DNA technique. The vector typically assists in replicating and/or expressing the inserted DNA sequence inside the host cell. Narration 00:00 … Vector. (PDF) What is a vector? - ResearchGate A vector is an animal that transmits a disease to other organisms. An insect that transmits a disease is known as an insect vector, and the disease it transmits is referred to as a vectorborne...
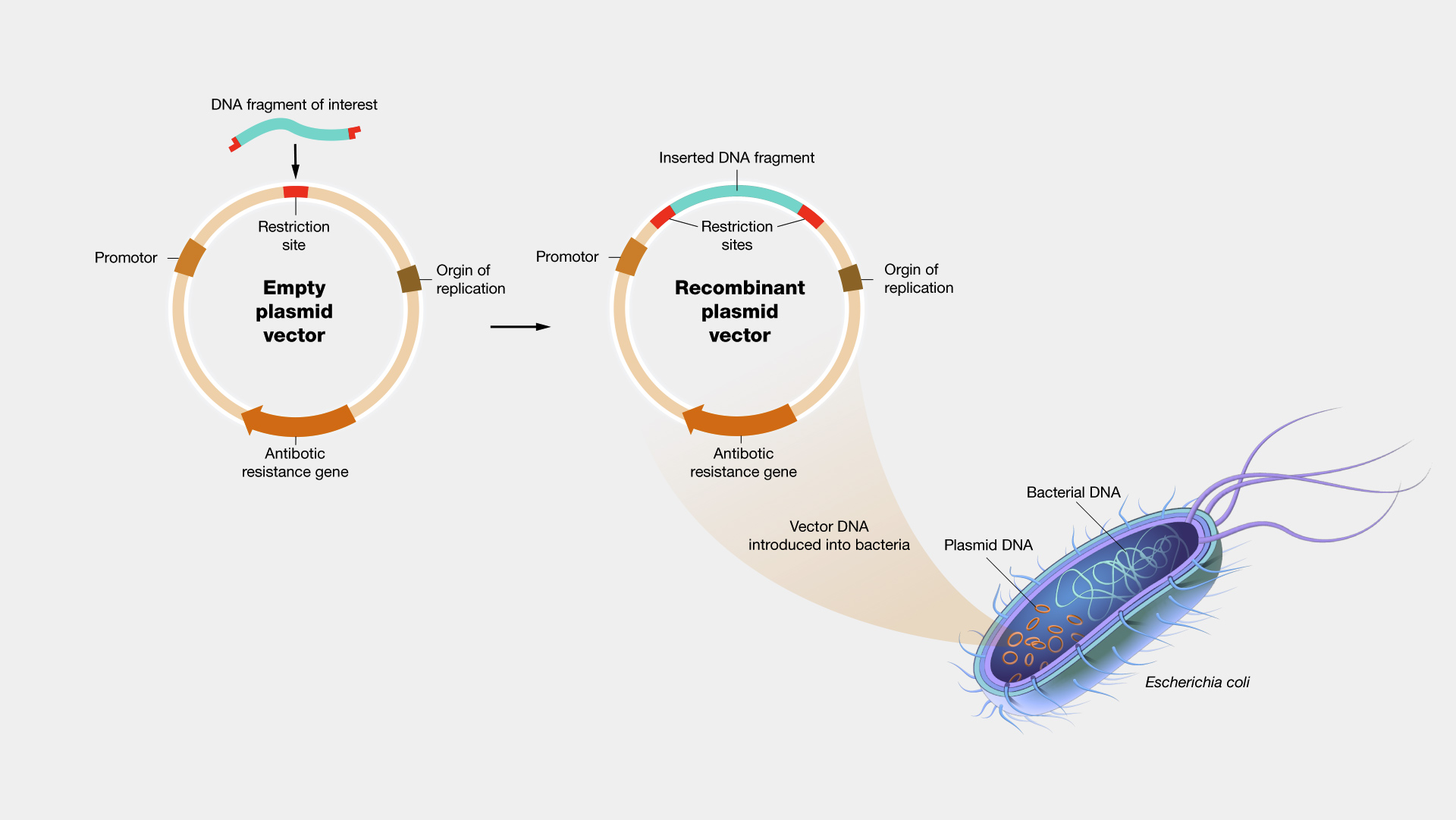
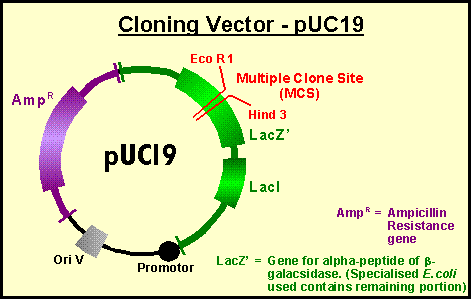
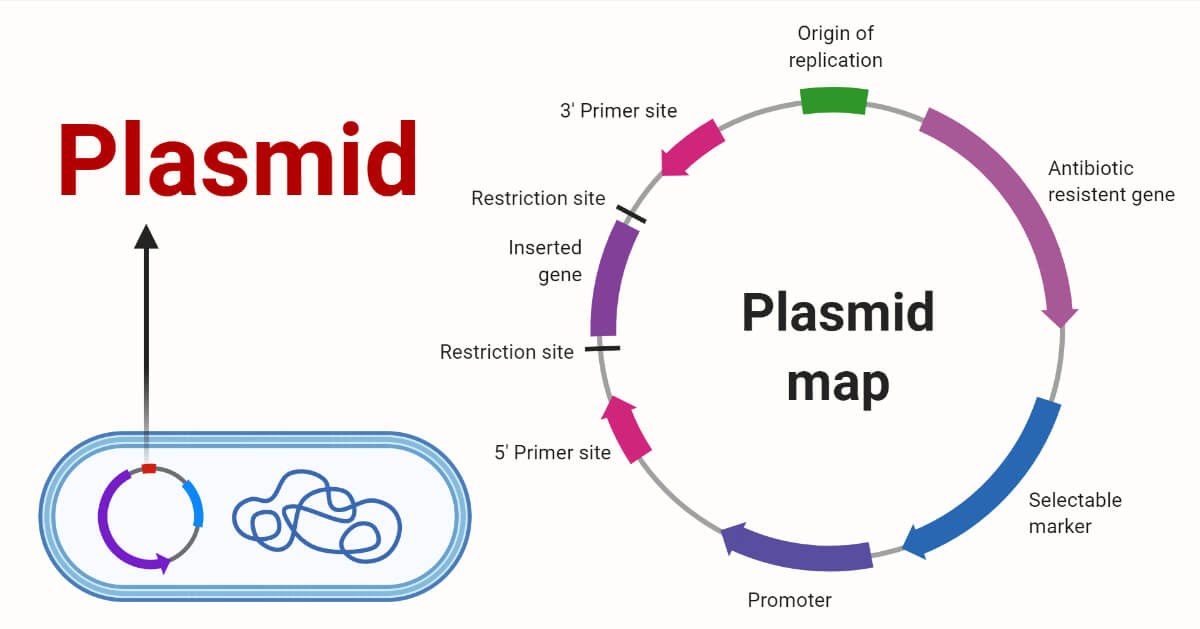
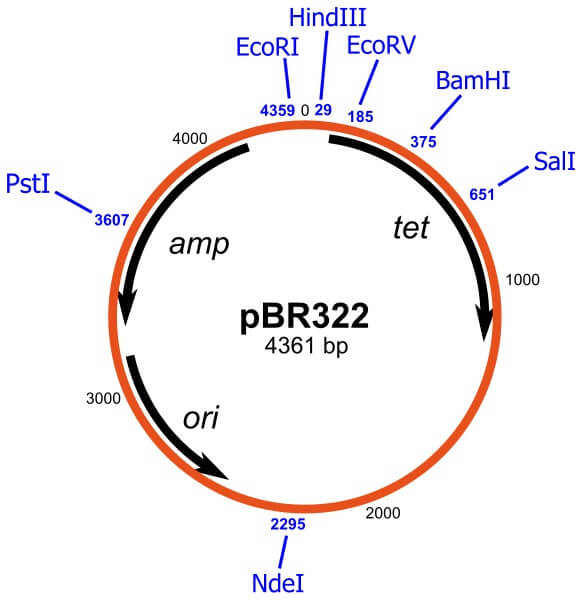
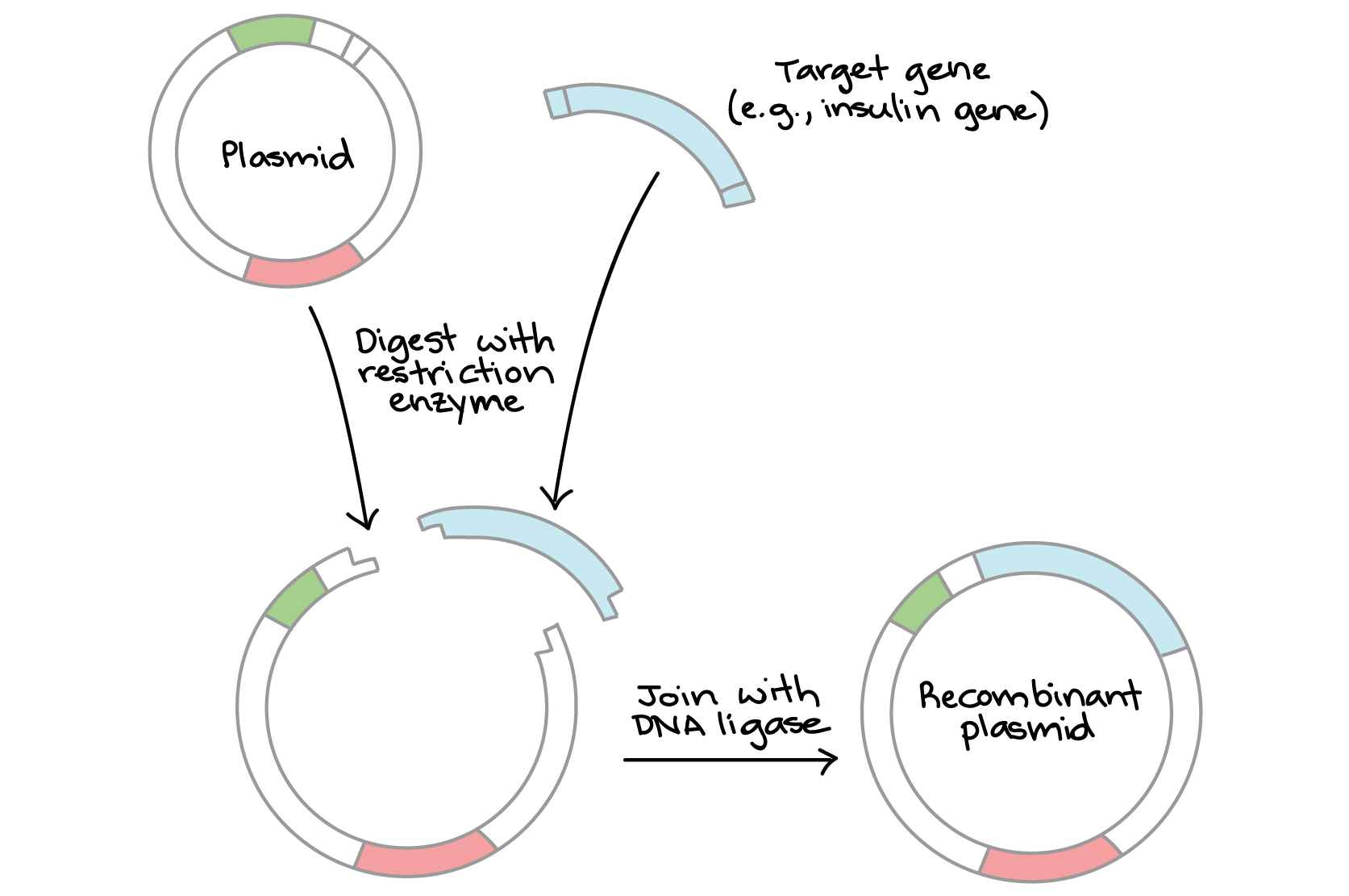
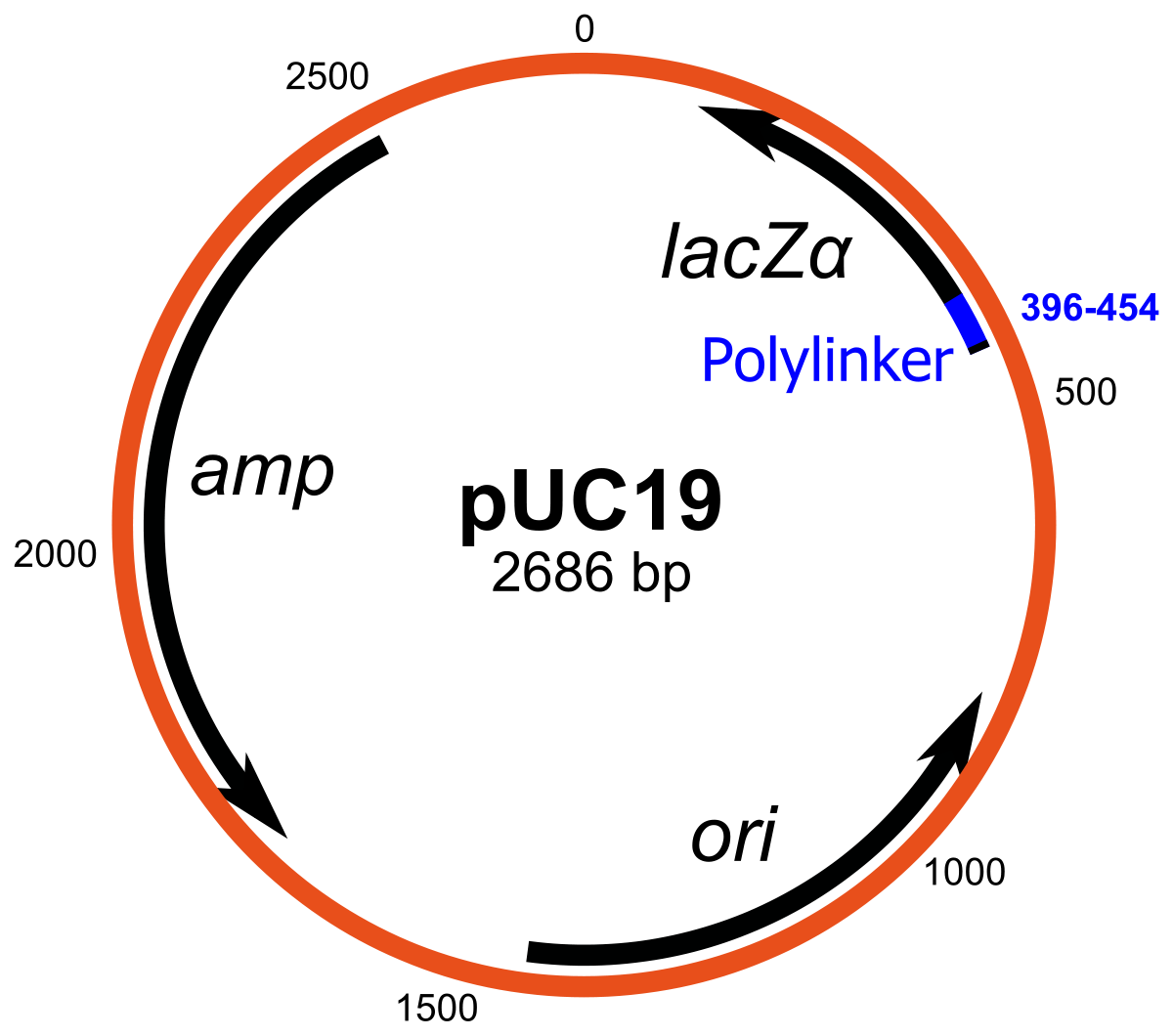
Vector | genetics | Britannica Other articles where vector is discussed: recombinant DNA: DNA cloning: …molecule is called a DNA vector (carrier). The most commonly used vectors are plasmids (circular DNA molecules that originated from bacteria), viruses, and yeast cells. Plasmids are not a part of the main cellular genome, but they can carry genes that provide the host cell with useful properties, such as…

Vector biology definition
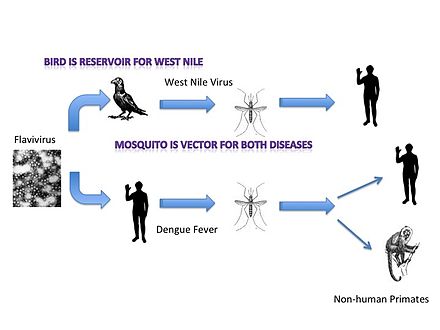
› dictionary › vectorVector Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary Sep 30, 2022 · A biological vector is an organism that transmits the causative agent or disease -causing organism from the reservoir to the host. It may also refer to a reproductive agent, dispersing reproductive structures, such as a bee that serves as a vector in transmitting pollen to the stigma of a flower. Medical Definition of Vector - MedicineNet Vector: In medicine, a carrier of disease or of medication. For example, in malaria a mosquito is the vector that carries and transfers the infectious agent. In molecular biology, a vector may be a virus or a plasmid that carries a piece of foreign DNA to a host cell. CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE SLIDESHOW › research › vector-bioVector Biology - National Institute of Allergy and Infectious... Vector Biology. Arthropod vectors, including insects and ticks, can transmit infectious disease pathogens among humans or between animals and humans. Arthropod vectors are responsible for the spread and transmission of malaria, dengue fever, chikungunya, yellow fever, Zika, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and Lyme disease.
Vector biology definition. link.springer.com › referenceworkentry › 10Targeting Vector | SpringerLink Definition. A targeting vector is a recombinant DNA construct that consists of a selection cassette, tailored by DNA arms homologous to genomic DNA, which flanks critical elements of a target gene. When introduced into ES cell the targeting vector integrates into the ES‐cell genome via homologous recombination. Biological vector | definition of biological vector by Medical dictionary vector [ vek´tor] 1. a carrier, especially the animal (usually an arthropod) that transfers an infective agent from one host to another. Examples are the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite Plasmodium between humans, and the tsetse fly that carries trypanosomes from other animals to humans. › dictionary › vectorVector Definition & Meaning - Merriam-Webster vector noun vec· tor ˈvek-tər 1 : a quantity that has magnitude and direction and that is usually represented by a line segment with the given direction and with a length representing the magnitude 2 : an organism (as an insect) that carries and passes on a disease-causing microbe Medical Definition vector 1 of 2 noun vec· tor ˈvek-tər 1 openstax.org › books › microbiology16.3 Modes of Disease Transmission - Microbiology | OpenStax Vector Transmission Diseases can also be transmitted by a mechanical or biological vector, an animal (typically an arthropod) that carries the disease from one host to another. Mechanical transmission is facilitated by a mechanical vector, an animal that carries a pathogen from one host to another without being infected itself.
Pathogens - Communicable diseases - AQA - GCSE Biology (Single ... - BBC They infect a host, reproduce themselves or replicate if it is a virus, spread from their host and infect other organisms. They also all have structural adaptations that make them successful at... 260.650.01 Vector Biology and Vector-Borne Diseases, 2023 3rd term ... Vector Biology and Vector-Borne Diseases: Presents the principles of transmission of human and animal pathogens by insects, mites and ticks. Covers basic arthropod biology with special attention to biological properties of vectors and their interactions with pathogens, basic components of arbopathogen disease cycles and principles of pathogen transmission dynamics. What is a Vector in Biology? - Study.com Vectors are living organisms that transmit diseases between individuals. It is important to note that the term "vector" can have multiple meanings. For instance, a vector may be represented as... Vector- Definition, Features, Types, Examples, Applications, Limitations A vector is a substance, usually a piece of DNA that carries a sequence of DNA or other genetic material and introduces it into a new cell. Vectors act as vehicles to transfer genetic material from one cell to the other for different purposes like multiplying, expressing, or isolation.
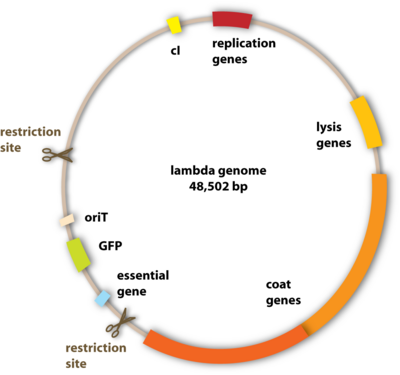
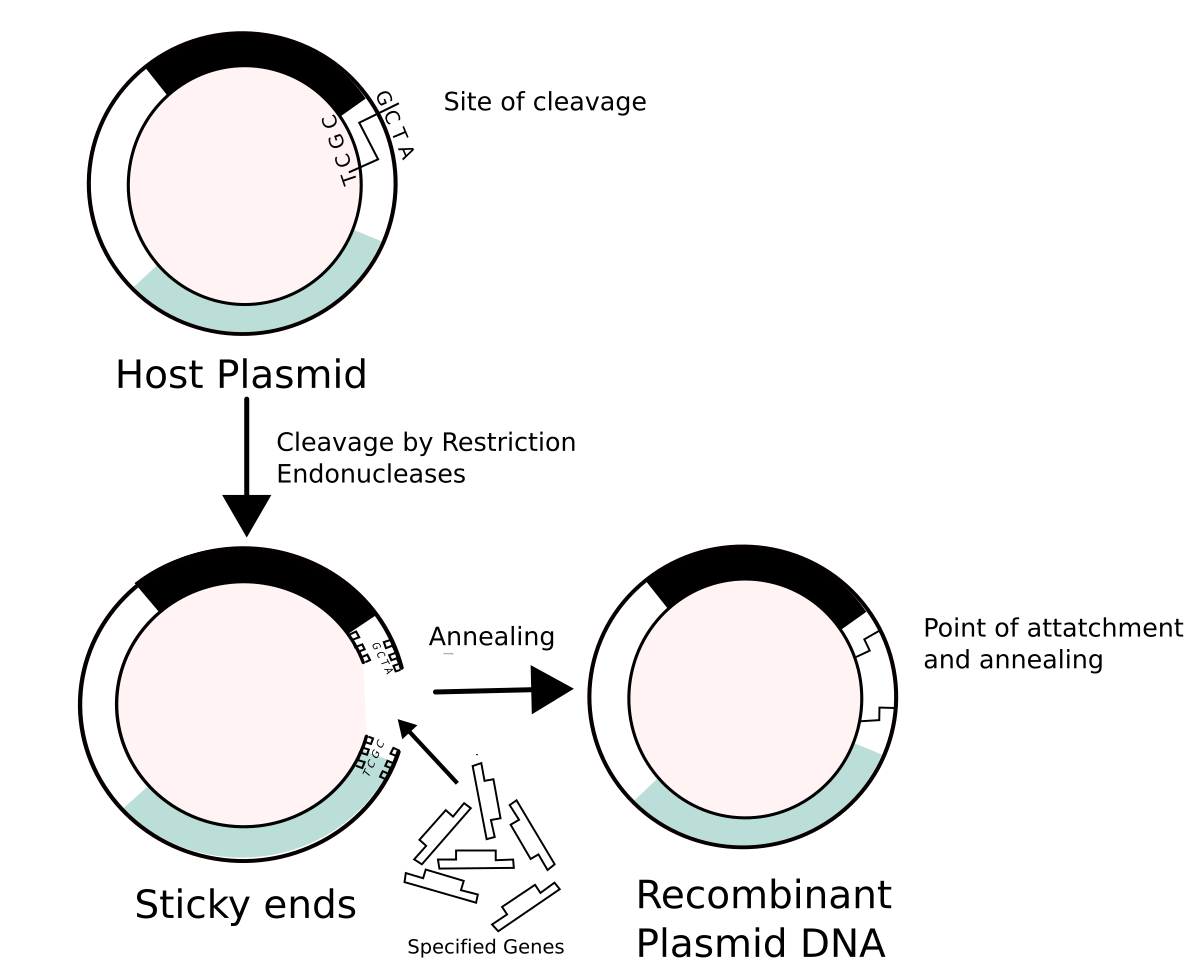
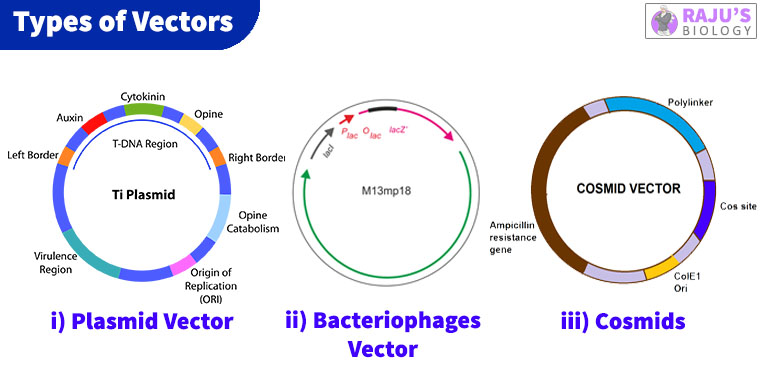
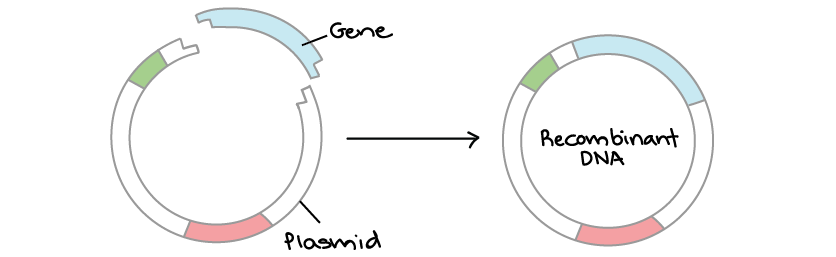
Vector (molecular biology) - Wikipedia In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle (e.g., plasmids, cosmids, Lambda phages) used as a vehicle to artificially carry a foreign nucleic sequence - usually DNA - into another cell, where it can be replicated and/or expressed. [1] A vector containing foreign DNA is termed recombinant DNA. medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com › Vector+(biology)Vector (biology) | definition of Vector (biology) by Medical ... vector [ vek´tor] 1. a carrier, especially the animal (usually an arthropod) that transfers an infective agent from one host to another. Examples are the mosquito that carries the malaria parasite Plasmodium between humans, and the tsetse fly that carries trypanosomes from other animals to humans. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Viral_vectorViral vector - Wikipedia Viral vectors are tools commonly used by molecular biologists to deliver genetic material into cells. This process can be performed inside a living organism ( in vivo) or in cell culture ( in vitro ). Viruses have evolved specialized molecular mechanisms to efficiently transport their genomes inside the cells they infect. royalsocietypublishing.org › doi › 10What is a vector? | Philosophical Transactions of the Royal... Mar 13, 2017 · 2. An overview of existing definitions of ‘vector’ One of the broadest definitions defines a vector as any organism (vertebrate or invertebrate) that functions as a carrier of an infectious agent between organisms of a different species [].This includes organisms playing a purely mechanical role in transmission (e.g. Musca flies in the transmission of Chlamydia trachomatis, the causative ...
byjus.com › biology › what-does-a-vector-mean-in-biologyWhat Does a Vector Mean in Biology? - BYJU'S Biology A biological vector is a living thing that carries the disease-causing agent or causative organism from reservoirs to the host. It could also be a reproductive agent that disperses reproductive components, such as a bee that acts as a pollen carrier for transferring pollen to a flower’s stigma.
Vector Definition in Science - ThoughtCo In the biological sciences, the term vector refers to an organism that transmits a disease, parasite, or genetic information from one species to another. Examples: Mosquitoes are a vector of malaria. A virus may be used as a vector to insert genes into a bacterial cell.
Vector (biology) - ScienceDaily Traditionally in medicine, a vector is an organism that does not cause disease itself but which spreads infection by conveying pathogens from one host to another. Note: The above text is...
Vector Definition & Meaning | Britannica Dictionary Britannica Dictionary definition of VECTOR. [count] 1. mathematics : a quantity (such as velocity) that has size and direction. 2. technical : the course or direction of an airplane. 3. biology : an insect, animal, etc., that carries germs that cause disease. a mosquito that is the principal vector of yellow fever.
National Center for Biotechnology Information National Center for Biotechnology Information
› research › vector-bioVector Biology - National Institute of Allergy and Infectious... Vector Biology. Arthropod vectors, including insects and ticks, can transmit infectious disease pathogens among humans or between animals and humans. Arthropod vectors are responsible for the spread and transmission of malaria, dengue fever, chikungunya, yellow fever, Zika, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and Lyme disease.
Medical Definition of Vector - MedicineNet Vector: In medicine, a carrier of disease or of medication. For example, in malaria a mosquito is the vector that carries and transfers the infectious agent. In molecular biology, a vector may be a virus or a plasmid that carries a piece of foreign DNA to a host cell. CONTINUE SCROLLING OR CLICK HERE SLIDESHOW
› dictionary › vectorVector Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary Sep 30, 2022 · A biological vector is an organism that transmits the causative agent or disease -causing organism from the reservoir to the host. It may also refer to a reproductive agent, dispersing reproductive structures, such as a bee that serves as a vector in transmitting pollen to the stigma of a flower.






















Post a Comment for "39 vector biology definition"