41 label the carrier proteins in model 3
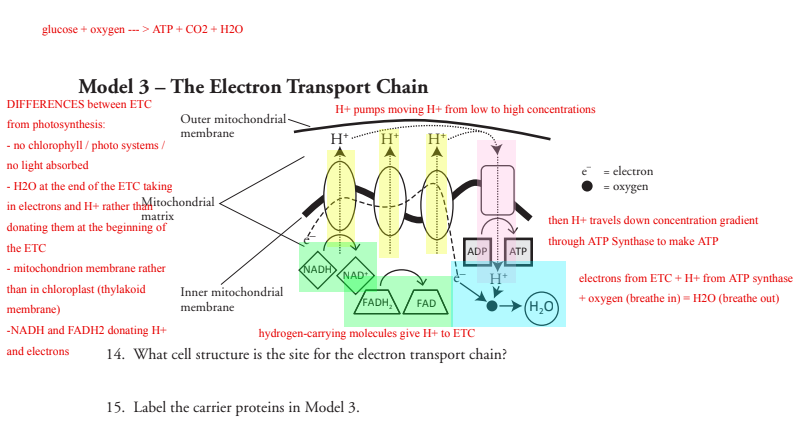
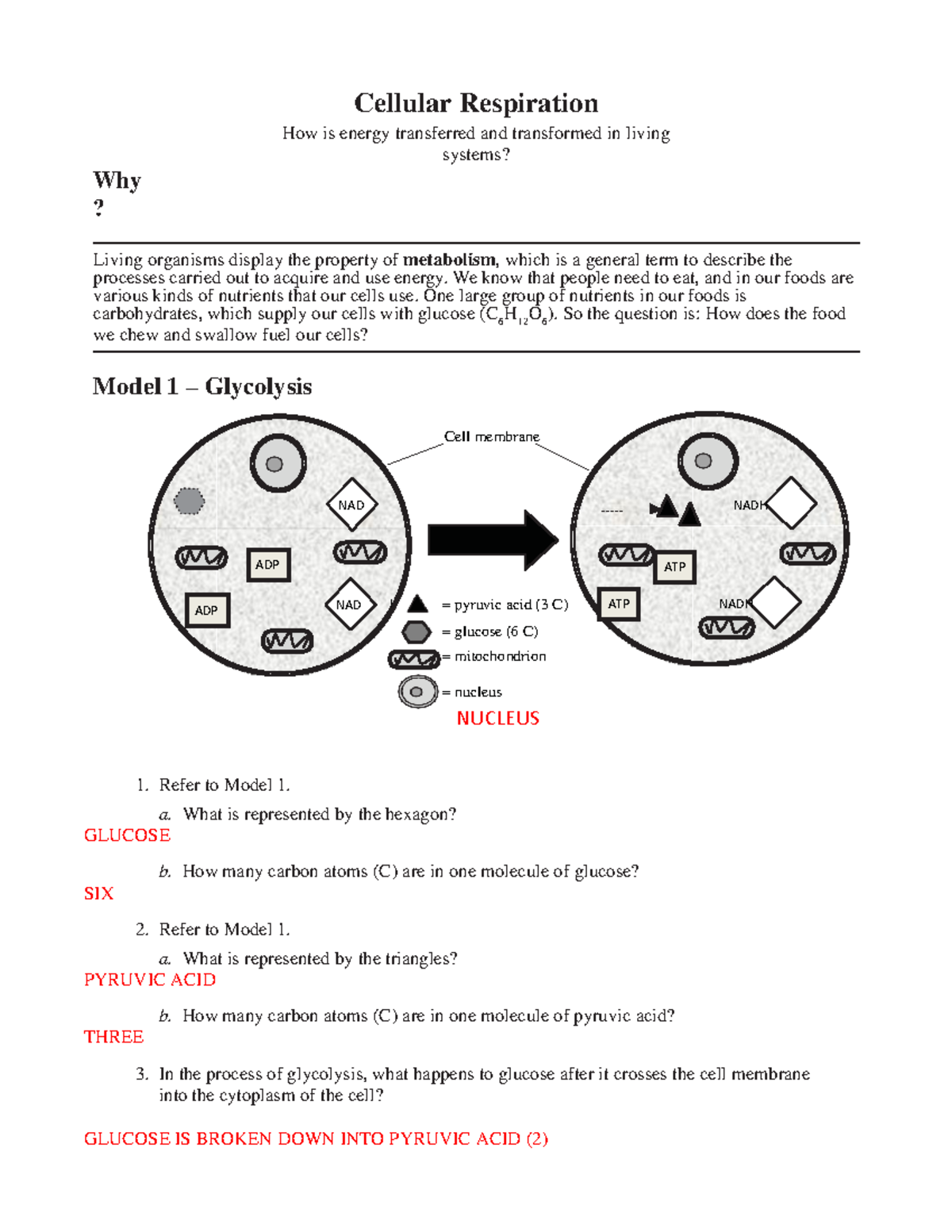
Multiple binding sites for [125I]RTI-121 and other cocaine analogs in ... In an effort to identify novel binding sites for cocaine and its analogs, we carried out binding studies with the high-affinity and selective ligand [125I]RTI-121 in rat frontal cortical tissue. Very low densities of binding sites were found. Saturation analysis revealed that the binding was to both … PDF Model 1 Glycolysis - psd202.org Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
PDF 3 Protein Structure-S - Norwell High School With your group, write a grammatically correct sentence that summarizes how the secondary protein structure is formed from the primary structure. Protein Structure 5 Model 3 - Protein Structure (Part B) Tertiary Structure H CH 2 CH 3CH 3 CH
Label the carrier proteins in model 3
PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - Washington Township Public School District 9. What name is given to the transmembrane proteins that allow this direct passage? 3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP. Cellular Respiration.docx - Cellular Respiration How is... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innermitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported acrossthe inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. Proteins in Plasma Membranes | Cell Transport - Nigerian Scholars The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. Carbohydrates attached to lipids (glycolipids) and to proteins (glycoproteins) extend from the outward-facing surface of the membrane. Image Attribution: OpenStax Biology.
Label the carrier proteins in model 3. Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer | Chegg.com Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innet mitochondrial Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain Outer mitochondrial membrane H Н. H incon oxygen Mitochondrial matrix AD GUADINAD Inner mitochondrial membrane ADH FAD (H.0 14. carrier protein Flashcards | Quizlet carrier protein Proteins that change shape to allow a substance to pass through the plasma membrane phagocytosis the engulfing of food by a cell facilitated diffusion Facilitated Diffusiona passive form of carrier transport exocytosis the process by which wastes are packaged in vesicles and leave the cell active transport Channel Protein: Definition, Function, Examples - Biology Dictionary Carrier proteins, proteins which bind and transport molecules across the membrane, are also involved in facilitated diffusion. Large molecules like glucose cannot pass through the narrow passageway created by channel proteins. Carrier proteins known as uniporters bind to glucose molecules one at a time. PDF ATP—The Free Energy Carrier - John A. Ferguson Senior High School Model 3 - The ATP Cycle ATP + water ADP + phosphate Respiration Energy Energy or photosynthesis Cellular processes such as muscle contraction, protein synthesis, cell division, etc. 9. Label the two large arrows in Model 3 with "hydrolysis" and "phosphorylation." 10. When ATP is hydrolyzed, free energy is available. a.
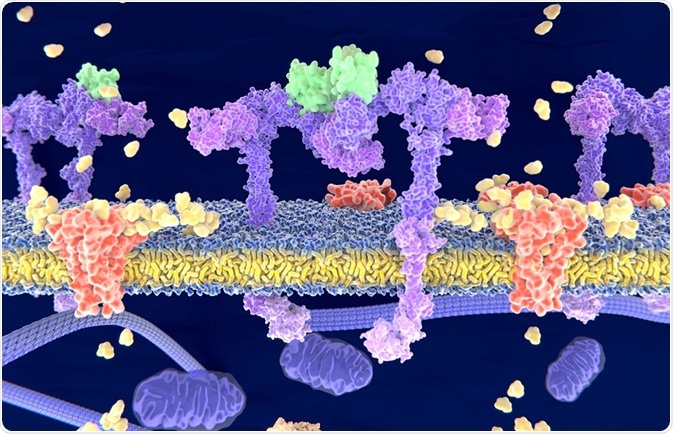
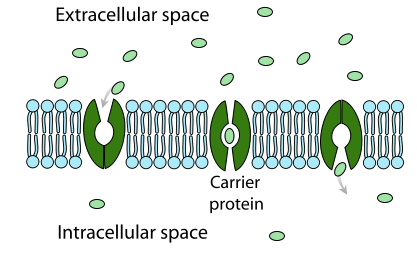
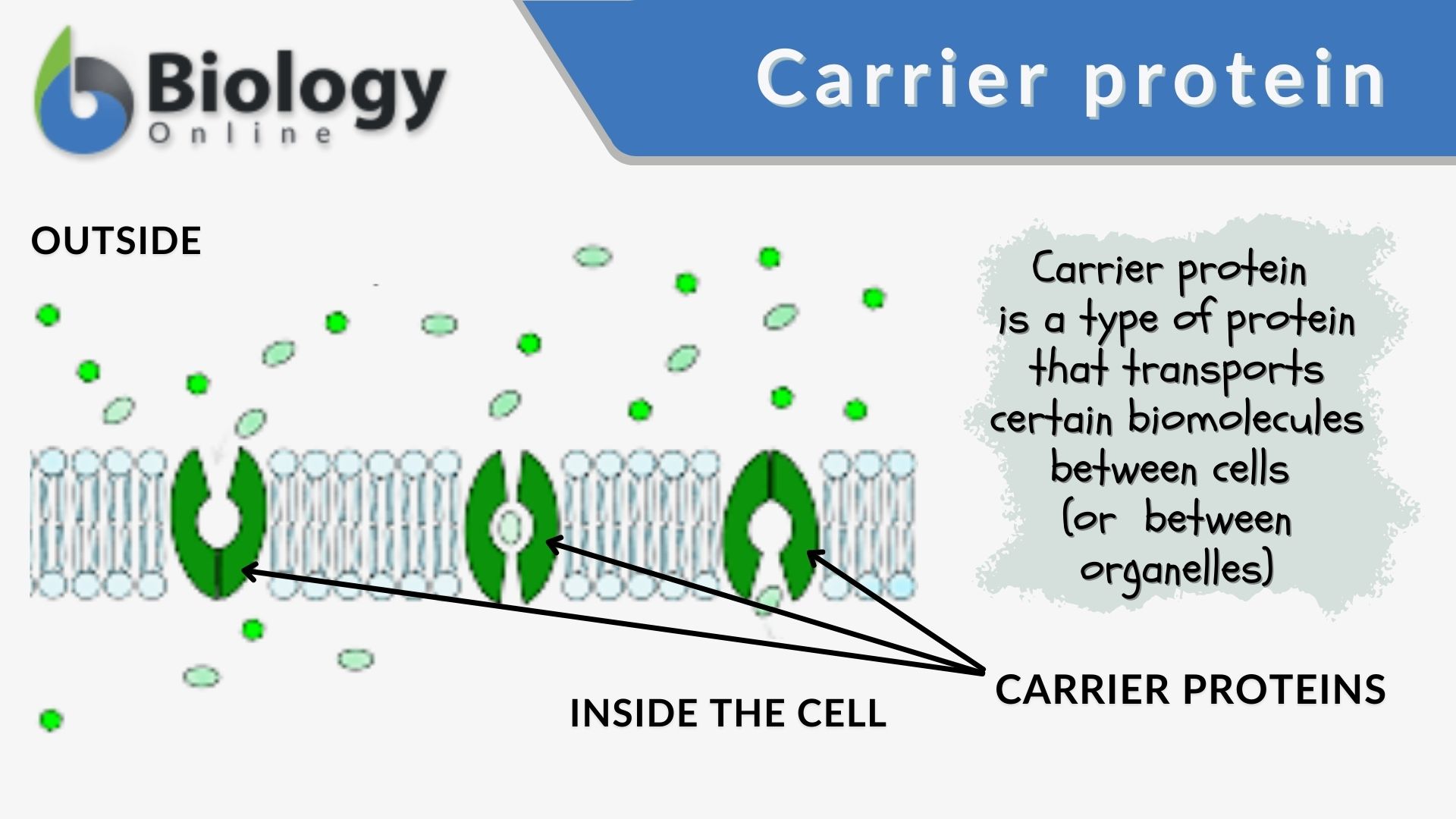
H 2 o model 3 the electron transport chain outer - Course Hero Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? HYDROGEN IONS (H+) HYDROGEN IONS ( H+ ) Read This! NADH and FADH 2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported acrossthe inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. Cellular uptake of the antitumor agent Dp44mT occurs via a carrier ... The chelator di-2-pyridylketone 4,4-dimethyl-3-thiosemicarbazone (Dp44mT) shows potent and selective anticancer and antimetastatic activity. However, the mechanism by which it is initially transported into cells to induce cytotoxicity is unknown. Hence, the current investigation examined the cellular uptake of ¹⁴C-Dp44mT relative to two ... Sterol carrier protein-x gene and effects of sterol carrier protein-2 ... Figure 3 shows that a protein similar to the molecular weight of 14 kDa (the predicated molecular weight of MsSCP-2 is 14,134 Da) was detected by anti-AeSCP-x antibodies, suggesting that M. sexta may have a SCP-2 analog. Carrier Proteins and Active Membrane Transport This schematic diagram shows carrier proteins functioning as uniporters, symporters, and antiporters. The tight coupling between the transport of two solutes allows these carriers to harvest the energy stored in the electrochemical gradient of one solute, typically an ion, to transport the other.
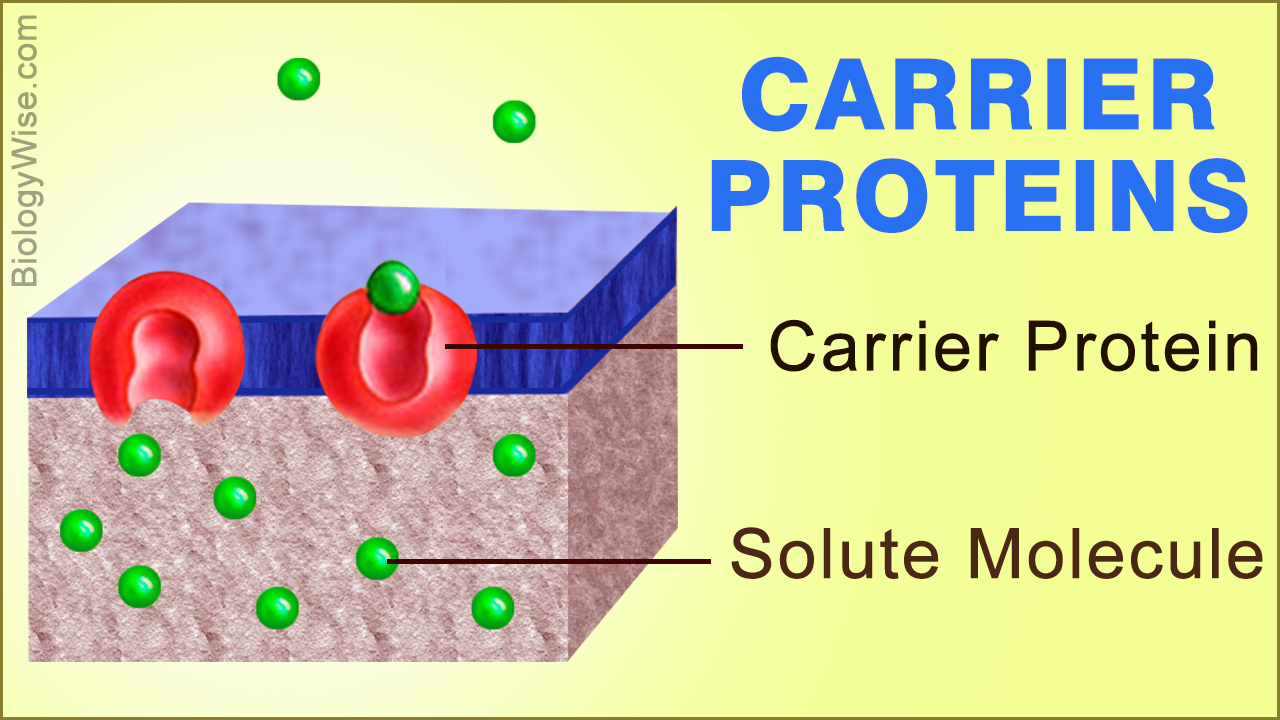
Channel Protein Functions and Examples - Study.com Learn about the channel protein's function, examples of channel proteins, carrier proteins, and facilitated diffusion. Updated: 01/18/2022 Table of Contents Biology A: Unit 3 Flashcards | Quizlet Channel proteins move substances across the membrane at a much faster rate than carrier proteins. Carrier proteins can allow much larger substances to cross the membrane than channel proteins do. Which type of transport does not require energy but uses carrier proteins to help move substances across the cell membrane? PDF Phospholipid & Membrane Transport Kit Student Handout 3 You will use a simplified representation of the phospholipid bilayer in this activity. 1. Label thehydrophilic headand hydrophobic tailin the photos below. CPK Color Scheme Oxygen (red) Nitrogen (blue) Hydrogen (white) Carbon (grey) Phosphorus (yellow) Center area is a convenient way to hold the phospholipids together to form membranes. Solved Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell - Chegg Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. (Which ones are the cytochromes?) 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the Question: Model 3 - The Electron Transport Chain H Η' Η' cell wall dectron oxygen cell membrane ADP ATP NADH NAD FADH FAD (HO) 14. What cell structure is the site for the electron transport chain?
13 Cellular Respiration-S - North Kitsap School District Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the inner mitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2 molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported across the inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons. The result of these multiple processes is the production of large
32 questions with answers in CARRIER PROTEINS | Science topic Mix the bacteria and protein together, incubate for a little while, spin down the bacteria, and measure the loss of the protein from the supernatant. Another method would be to attach a fluorescent...
PDF Chapter 5: Cell Membranes and Signaling - Northern Highlands Regional ... Membrane proteins are the mosaic part of the model. Describe each of the two main categories: integral proteins peripheral ... - 3 - 10. Label the following structures: Glycolipid, glycoprotein, integral protein, peripheral protein, cholesterol ... carrier protein, simple diffusion. For each type of transport, give an example of a ...
GMP Recombinant Human IL-6 (carrier-free), IL-6 - BioLegend Stock solutions can also be prepared at 50 - 100 µg/mL in appropriate sterile buffer, carrier protein such as 0.2 - 1% endotoxin-free BSA or HSA can be added when preparing the stock solution. Aliquots can be stored between 2°C and 8°C for up to one week or stored at -20°C or colder for up to 3 months. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
PDF PROTEINS: THREE-DIMENSIONAL STRUCTURE - Stanford University ture and that the enzymatic activities of certain crystallized proteins were due to unknown entities associated with an inert protein carrier. In 1934, J.D. Bernal and Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin showed that a crystal of the protein pepsinyielded a discrete diffraction pattern when placed in an X-ray beam.
Carrier Protein - Definition, Function and Examples - Biology Dictionary Carrier Protein Definition Carrier proteins are proteins that carry substances from one side of a biological membrane to the other. Many carrier proteins are found in a cell 's membrane, though they may also be found in the membranes of internal organelles such as the mitochondria, chloroplasts, nucleolus, and others.
PDF Protein Structure - Weebly Model 3 - Protein Structure (Part B) CH ____________________________ structure involves multiple polypeptide chains interacting. Ionic and hydrogen bonds can occur as well as disulfide bridges and hydrophobic interactions. CH Protein Structure 5 Tertiary Structure H CH 2 3CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH CH (CH 2) 4NH
Structure of the Membrane | Biology for Majors I - Lumen Learning The plasma membrane is made up primarily of a bilayer of phospholipids with embedded proteins, carbohydrates, glycolipids, and glycoproteins, and, in animal cells, cholesterol. The amount of cholesterol in animal plasma membranes regulates the fluidity of the membrane and changes based on the temperature of the cell's environment.
PDF Leology - Welcome 5. icwer 6. mcre again and cycle re peaks trans 23. di C On the diagram below, add these labels: facilitated diffusion with a carrier protein, facilitated diffusion with a channel protein, simple-diffusion. For each type of transport, give an example of a material that is moved in this manner. — achvc carrier (qtutc3e 24.
The Cell Membrane | Anatomy and Physiology I - Lumen Learning The lipid bilayer forms the basis of the cell membrane, but it is peppered throughout with various proteins. Two different types of proteins that are commonly associated with the cell membrane are the integral proteins and peripheral protein (Figure 3). As its name suggests, an integral protein is a
PDF ATP—The Free Energy Carrier - Pedersen Science protein synthesis, cell division, etc. 9. Label the two large arrows in Model 3 with "hydrolysis" and "phosphorylation." 10. When ATP is hydrolyzed, free energy is available. a. According to Model 3, what does that energy get used for? b. Name at least two other cellular processes that could be fueled by the hydrolysis of ATP that
Proteins in Plasma Membranes | Cell Transport - Nigerian Scholars The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane describes the plasma membrane as a fluid combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, and proteins. Carbohydrates attached to lipids (glycolipids) and to proteins (glycoproteins) extend from the outward-facing surface of the membrane. Image Attribution: OpenStax Biology.
Cellular Respiration.docx - Cellular Respiration How is... Label the carrier proteins in Model 3. 16. What substance do the carrier proteins transport across the innermitochondrial membrane? Read This! NADH and FADH 2molecules release hydrogen ions that are transported acrossthe inner mitochondrial membrane with the help of electrons.
PDF Chapter 3 Review Materials Key - Washington Township Public School District 9. What name is given to the transmembrane proteins that allow this direct passage? 3. Figure 3.3 is a simplified diagram of the plasma membrane. Structure A repre- sents channel proteins constructing a pore, structure B represents an ATP- energized solute pump, and structure C is a transport protein that does not depend on energy from ATP.



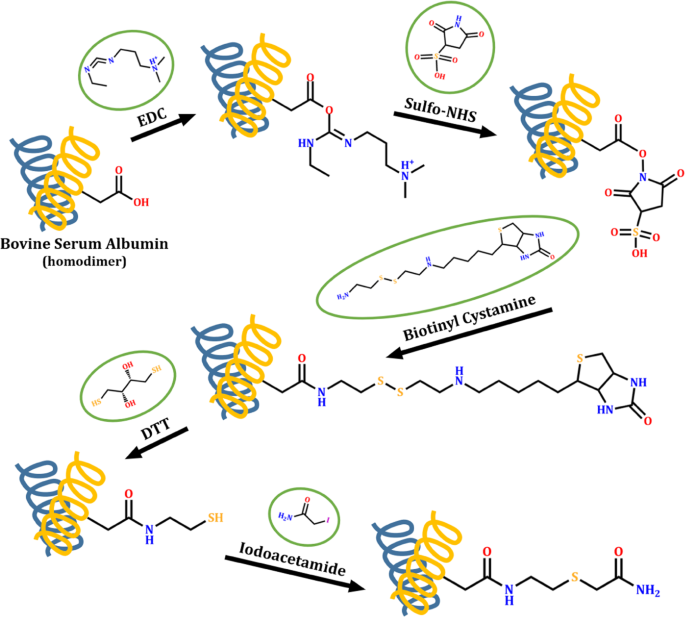















Post a Comment for "41 label the carrier proteins in model 3"